
Calcium is the most abundant mineral in the body and is required to build and maintain strong bones and healthy communication between the brain and other parts of the body. Asides from this, calcium regulates muscle contraction, including the beating of the heart muscle and is a co-factor for many enzymes.
Calcium continues to strengthen the bones of humans until the age of 20-25 when bone density is highest. After that age, bone density declines, but calcium continues to help maintain bones and slow down bone density loss, which is a natural part of the aging process. People who do not consume enough calcium before the age of 20-25 have a considerably higher risk of developing the brittle bone disease or osteoporosis later in life; this is because calcium is drawn from the bones as a reserve.


Different sources of calcium exist so how should one choose the proper one?
Properties to be considered :
· Bioavailability
· Calcium content
· Solubility
· Organoleptic characteristics
· Interaction with other ingredients
Organic source vs. Inorganic Source
It is generally agreed that the bioavailability of organic salts is much higher than the bioavailability of inorganic salts. Based on literature it appears that the bioavailability of organic calcium is higher than that of inorganic calcium.
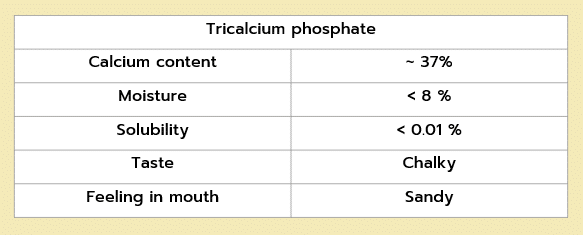
Tri Calcium Phosphate
provides an economical solution but has low bioavailability and a specific taste (chalky).
Organic Salts comparison
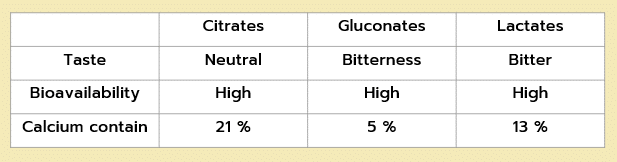
citrate-based calcium offers an advantage in mineral content and taste
Tri Calcium Citrate
provides an organic source of calcium with high bioavailability and high calcium content (especially when compared to inorganic sources such as phosphate and carbonate). Gadot’s calcium is based on citrates which are recognized as part of our body system and provide the most suitable organic mineral vehicles to achieve maximum absorption.
Only Calcium Citrate – does not cause the formation of kidney stones.
Only Calcium Citrate’s absorption is independent of timing (before/after meal).
Calcium Citrate vs. Calcium carbonate

- Related products :
- Calcium citrate